Spotting in Pregnancy | Causes and Caution
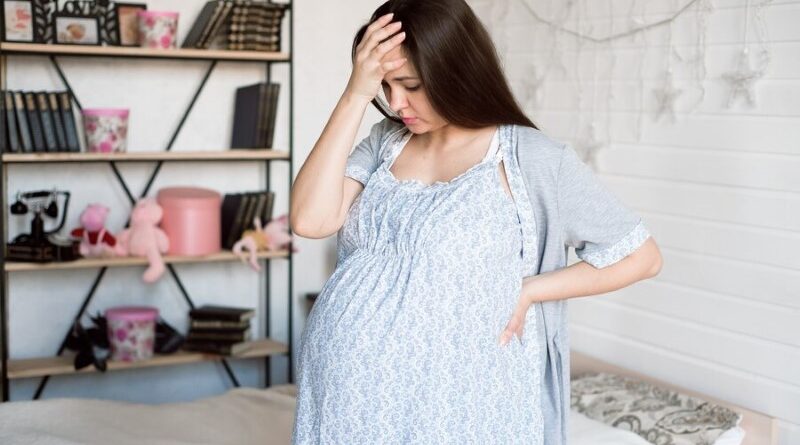
Spotting in Pregnancy | Causes and Caution, Pregnancy is a remarkable journey filled with anticipation and excitement. However, it can also bring about moments of concern and uncertainty, especially when unexpected symptoms arise. One such sign is spotting, the appearance of light vaginal bleeding during pregnancy. While spotting doesn’t always indicate a serious issue, it’s important for expectant mothers to understand its potential causes and exercise caution when confronted with this situation.
Understanding Spotting in Pregnancy

Spotting refers to the occurrence of slight vaginal bleeding that is lighter than a regular menstrual period. It typically presents as pink, brown, or light red blood on toilet tissue, underwear, or a panty liner. Unlike heavy bleeding, spotting usually doesn’t require a sanitary pad.
Common Causes of Spotting During Pregnancy
- Implantation Bleeding: This occurs when the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining, causing minor irritation and resulting in light spotting. It usually happens around the time a woman would expect her period.
- Cervical Changes: Pregnancy hormones can lead to increased blood flow to the cervix, making it more sensitive and prone to bleeding, especially after intercourse or a pelvic exam.
- Miscarriage: Unfortunately, spotting can sometimes indicate a miscarriage, particularly during the first trimester. It might be accompanied by abdominal pain and cramping.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: When a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube, it can cause bleeding and requires immediate medical attention.
- Molar Pregnancy: A rare abnormality where tissue grows in the uterus instead of a fetus. This can lead to spotting along with other symptoms such as severe nausea and a larger-than-normal uterus.
- Infections: Infections of the cervix or vaginal area can lead to spotting. It’s important to address infections promptly to prevent complications.
- Subchorionic Hematoma: Blood can pool between the uterine wall and the placenta, causing spotting. Most cases resolve on their own, but medical monitoring is advisable.
- Cervical Polyps: These non-cancerous growths on the cervix can become irritated during pregnancy and cause spotting.
- Vaginal Dryness: Hormonal changes can lead to dryness and spotting. Using a water-based lubricant can help alleviate this discomfort.
When to Exercise Caution
Spotting in Pregnancy can be benign, but there are instances where it’s essential to exercise caution and seek medical attention promptly:
- Heavy Bleeding: If the bleeding becomes rich, akin to a regular period or more, it might signify a miscarriage or other complications.
- Severe Pain: Intense abdominal or pelvic pain accompanied by spotting could indicate an ectopic pregnancy or other serious conditions.
- Clotting: Passing blood clots, especially large ones, could suggest a miscarriage or other medical issues.
- Dizziness and Fainting: If spotting is coupled with dizziness or fainting, it might signify low blood pressure or anemia.
- Fever and Chills: These symptoms along with spotting might point towards an infection that needs medical attention.
- Lack of Fetal Movement: If spotting occurs along with a noticeable reduction in fetal movement, consult a healthcare provider.
Seeking Medical Advice
Spotting in Pregnancy, Pregnant women should never hesitate to contact their healthcare provider when experiencing spotting, especially if any of the aforementioned cautionary signs are present. A medical professional can provide personalized guidance, conduct necessary tests, and determine the appropriate steps to take.
Diagnosis and Tests
When consulting a healthcare provider about spotting, several diagnostic approaches might be taken:
- Ultrasound: A non-invasive imaging technique to visualize the uterus and fetus, helping identify potential causes of spotting.
- Blood Tests: Hormone levels and blood type might be assessed to understand the underlying cause of spotting.
- Pelvic Exam: To check for any visible issues with the cervix or vaginal area.
- HCG Monitoring: Serial Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) tests can help monitor the progress of a pregnancy and detect potential complications.
Preventive Measures
While not all causes of spotting can be prevented, there are steps expectant mothers can take to minimize their risk:
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly (as advised by your healthcare provider), and manage stress.
- Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Both can contribute to complications and should be avoided during pregnancy.
- Prenatal Care: Regular check-ups and following medical advice can help identify and address potential issues early.
- Safe Intercourse: If spotting occurs after intercourse, consult a healthcare provider to ensure it’s safe to continue sexual activity.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration and support overall health.
Spotting in Pregnancy can be alarming, but it’s not always a cause for panic. Understanding its potential causes and knowing when to seek medical attention is crucial for ensuring a healthy pregnancy. Every woman’s pregnancy journey is unique, and while some cases of spotting might resolve on their own, others might require medical intervention. By staying informed, maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, and being attentive to cautionary signs, expectant mothers can navigate the complexities of pregnancy with greater confidence and peace of mind.