Essential Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy: Tips, Symptoms, and Care
Are you expecting a bundle of joy? Congratulations! Pregnancy is an exciting and transformative journey in a woman’s life. To ensure a healthy and happy pregnancy, it’s essential to be well-informed and take proper care of yourself and your baby. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll provide you with valuable tips, insights, and information about pregnancy.
Pregnancy is a remarkable journey that brings new life into the world. It is a transformative experience for both the mother and the baby. Understanding the process of pregnancy is crucial to ensure a healthy and safe pregnancy.
What is Pregnancy?
Pregnancy is the period during which a fertilized egg develops into a baby inside a woman’s uterus. It begins with the process of conception, where a sperm fertilizes an egg, and the fertilized egg implants itself in the uterine lining. This marks the beginning of pregnancy.
How does pregnancy occur?
This is a fundamental question that many individuals have when it comes to understanding the process of conception and pregnancy. Let’s explore the steps involved in pregnancy.
Menstrual Cycle: Pregnancy begins with a woman’s menstrual cycle. Each month, the ovaries release an egg, a process called ovulation. The egg travels down the fallopian tube, waiting to be fertilized.
Sexual Intercourse: Pregnancy occurs when sperm from a man’s ejaculate enters a woman’s vagina during sexual intercourse. The sperm travel through the cervix and into the fallopian tubes, where fertilization can take place.
Fertilization: Fertilization happens when a sperm successfully penetrates the outer membrane of the egg. This usually occurs in the fallopian tube. Once fertilization occurs, the genetic material from the sperm and the egg combine to form a single cell called a zygote.
Implantation: After fertilization, the zygote begins to divide rapidly as it travels down the fallopian tube towards the uterus. Around 6-12 days after fertilization, the zygote reaches the uterus and undergoes implantation. It attaches to the uterine lining, known as the endometrium, and starts to establish a connection with the mother’s blood vessels.
Hormonal Changes: Implantation triggers hormonal changes in the woman’s body. The newly formed embryo produces a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which signals to the body that pregnancy has occurred. The presence of hCG is what pregnancy tests detect to confirm pregnancy.
Development of the Embryo: Once implanted, the zygote develops into an embryo. It receives nourishment and oxygen from the mother through the placenta, which forms as the embryo grows. The embryo undergoes various stages of development, including the formation of major organs and body structures.
Pregnancy Symptoms: As the embryo develops, the woman may begin to experience common pregnancy symptoms such as missed periods, breast tenderness, fatigue, nausea (morning sickness), frequent urination, and mood swings. These symptoms are a result of the hormonal changes taking place in the body.
Prenatal Care: Once pregnancy is confirmed, it is essential to seek prenatal care from healthcare professionals. Regular check-ups, monitoring of the baby’s growth, and necessary tests are performed to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the developing baby.
In conclusion, pregnancy occurs when a sperm fertilizes an egg, leading to the formation of a zygote. The zygote implants itself in the uterus, and with proper nurturing and development, it grows into an embryo. Understanding the process of pregnancy can help individuals make informed decisions about their reproductive health and seek appropriate care during this transformative period of life.
The Process of Conception and Implantation
The process of conception and implantation is a crucial step in the journey of pregnancy. It involves the fertilization of an egg by a sperm and the subsequent attachment of the fertilized egg to the lining of the uterus. Let’s delve into the details of this fascinating process.
Conception
Conception occurs when a sperm successfully fertilizes an egg. This usually happens during sexual intercourse, where millions of sperm are ejaculated into the vagina. The sperm then swim through the cervix and into the fallopian tubes, where the egg awaits fertilization.
Fertilization: Fertilization occurs when a sperm penetrates the outer layer of the egg, leading to the fusion of genetic material from both the sperm and the egg. This forms a single-cell embryo known as a zygote. The genetic material contains the instructions for the development of the baby.
Implantation
After fertilization, the zygote travels down the fallopian tube towards the uterus. During this journey, the zygote undergoes several divisions, forming a ball of cells called a blastocyst. Approximately 5-7 days after fertilization, the blastocyst reaches the uterus.
Implantation occurs when the blastocyst attaches itself to the uterine lining, known as the endometrium. The blastocyst burrows into the endometrium, establishing a connection with the mother’s blood vessels. This connection allows the exchange of nutrients and waste products between the mother and the developing embryo.
Signs of Implantation
Implantation may cause some mild symptoms in some women, although many may not notice any noticeable signs. Some women may experience light spotting or cramping around the time of implantation. This is known as implantation bleeding and is typically lighter and shorter in duration than a regular period.
Timing of Implantation
Implantation usually occurs around 6-12 days after fertilization, but it can vary from woman to woman. It is often accompanied by hormonal changes in the body, including an increase in the hormone progesterone, which supports the pregnancy.
Confirmation of Pregnancy
Implantation is a significant milestone in pregnancy, and it marks the beginning of the body’s production of the pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Detection of hCG in the urine or blood is the basis for pregnancy tests, which can confirm pregnancy a few days after implantation.
The process of conception and implantation is a remarkable sequence of events that leads to the beginning of a new life. Understanding these processes can help individuals appreciate the complexity and beauty of human reproduction. If you suspect you might be pregnant or have concerns about conception and implantation, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide guidance and support throughout your pregnancy journey.
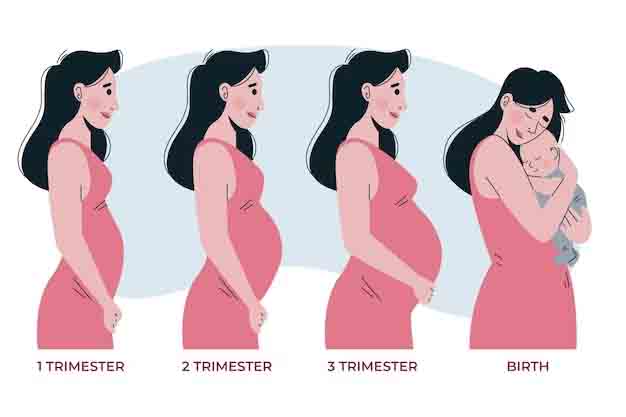
Different Stages of Pregnancy
Pregnancy is divided into three trimesters, each with its unique characteristics and developments.
The First Trimester (Weeks 1-12)
The first trimester is a critical period as the embryo undergoes rapid growth and development. During this time, major organs and body systems begin to form. Hormonal changes in the body can lead to various early signs of pregnancy, such as missed periods, breast tenderness, and morning sickness.
The Second Trimester (Weeks 13-27)
The second trimester is often referred to as the “golden period” of pregnancy. By this time, the baby’s organs are well-formed, and its sex can be determined. The mother may experience physical changes like a growing belly and increased energy. It is also a time when the mother can feel the baby’s movements for the first time.
The Third Trimester (Weeks 28-40)
The third trimester is the final stage of pregnancy, characterized by the baby’s rapid growth and preparation for birth. The mother may experience discomfort due to the increased size of the baby and the pressure on her organs. It is essential to monitor the baby’s movements during this time.
Calculating your due date

Calculating your due date is an essential step in pregnancy as it helps you anticipate the arrival of your baby. Here’s how you can calculate your due date:
First Day of Last Menstrual Period (LMP) Method: This is the most common method used by healthcare providers. Start by identifying the first day of your last menstrual period and count forward 280 days or 40 weeks. This method assumes a regular 28-day menstrual cycle and ovulation occurring on day 14. However, keep in mind that not all women have a 28-day cycle or ovulate on day 14.
Ovulation Method: If you know the date of ovulation, you can add 266 days to it to estimate your due date. Ovulation typically occurs around two weeks after the start of your menstrual cycle.
Ultrasound Method: An ultrasound can provide an accurate estimation of your due date by measuring the size of the fetus. The ultrasound is usually performed in the first trimester when the baby’s size is most predictable.
It’s important to note that these methods provide an estimated due date, and your baby may arrive a few weeks before or after the calculated date. Additionally, your healthcare provider will monitor your pregnancy and may adjust the due date based on the baby’s growth and development.
Remember, the due date is an approximate date, and the actual timing of birth may vary. Stay in close communication with your healthcare provider for the most accurate estimation of your due date.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Pregnancy
Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of pregnancy is crucial for early detection and appropriate prenatal care. Some common early signs include a missed period, breast changes, nausea, fatigue, and food cravings or aversions. These symptoms occur due to hormonal changes in the body.
Early signs and symptoms of pregnancy can vary from woman to woman, and some may experience them while others may not. These early signs often occur within the first few weeks after conception and can include:
Missed Period: One of the first signs of pregnancy is a missed period. If you have regular menstrual cycles and your period is late, it could indicate pregnancy.
Breast Changes: Your breasts may become tender, swollen, or sensitive. The areolas (the area around the nipples) may darken, and you may notice visible veins on your breasts.
Fatigue: Feeling excessively tired or fatigued is common during early pregnancy. Hormonal changes and increased blood production can contribute to this fatigue.
Nausea and Morning Sickness: Nausea, often accompanied by vomiting, is commonly referred to as morning sickness. It can occur at any time of the day and may be triggered by certain smells or foods.
Increased Urination: You may find yourself urinating more frequently due to the increased blood flow to the kidneys and the expanding uterus putting pressure on the bladder.
Food Cravings or Aversions: Some women develop cravings for certain foods or experience aversions to foods they once enjoyed. These changes in taste preferences are thought to be influenced by hormonal shifts.
Mood Swings: Hormonal fluctuations can lead to mood swings, irritability, or increased emotional sensitivity.
Frequent Headaches: Headaches can be a common symptom of early pregnancy due to hormonal changes and increased blood circulation.
Heightened Sense of Smell: You may become more sensitive to odors, and certain smells that previously went unnoticed may suddenly become overpowering.
Bloating and Constipation: Hormonal changes can slow down digestion, leading to bloating and constipation.
It’s important to remember that these symptoms can also be attributed to other factors, and the presence of these signs does not guarantee pregnancy. If you suspect you may be pregnant, it’s advisable to take a home pregnancy test or consult with your healthcare provider for confirmation.
Prenatal Care and Health
Prenatal care is an essential aspect of maintaining a healthy pregnancy and ensuring the well-being of both the mother and the developing baby. It involves regular medical check-ups, screenings, and lifestyle adjustments to promote a healthy pregnancy. Here are some key aspects of prenatal care and maintaining good health during pregnancy:
Choosing a Healthcare Provider: It’s important to select a healthcare provider, such as an obstetrician or midwife, who specializes in prenatal care. They will monitor the progress of your pregnancy and provide guidance and support.
Regular Check-ups: Prenatal care involves regular visits to your healthcare provider throughout the pregnancy. These check-ups allow for monitoring of your health, the growth and development of the baby, and the early detection of any potential issues.
Blood Tests and Screenings: Blood tests are conducted to check for various factors, including blood type, Rh factor, iron levels, and potential infections. Additional screenings, such as genetic testing and ultrasound examinations, may be recommended based on your medical history and risk factors.
Healthy Diet and Nutrition: A well-balanced diet is crucial for the proper development of the baby and the overall health of the mother. It’s important to consume a variety of nutritious foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products. Certain nutrients like folic acid, iron, and calcium are particularly important during pregnancy and may be supplemented.
Exercise and Physical Activity: Staying physically active during pregnancy can help improve circulation, reduce discomfort, and enhance overall well-being. However, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine which exercises are safe and appropriate for you.
Managing Weight Gain: Weight gain during pregnancy is normal and necessary for the baby’s growth. Your healthcare provider will guide you on appropriate weight gain based on your pre-pregnancy weight and overall health. Excessive weight gain or insufficient weight gain can both have potential risks, so it’s important to follow the recommended guidelines.
Managing Discomforts: Pregnancy can bring about various discomforts like nausea, backache, heartburn, and fatigue. Your healthcare provider can suggest remedies and lifestyle adjustments to alleviate these discomforts and improve your overall comfort.
Avoiding Harmful Substances: It’s crucial to avoid substances that can harm the developing baby, such as alcohol, tobacco, illicit drugs, and certain medications not approved by your healthcare provider. These substances can have severe negative effects on the baby’s growth and development.
Emotional and Mental Well-being: Pregnancy can bring about emotional and mental changes. It’s important to prioritize self-care, seek support from loved ones, and communicate any concerns or challenges with your healthcare provider. Counseling or support groups may also be beneficial.
Education and Preparation: Prenatal care involves educating yourself about pregnancy, childbirth, and newborn care. Attend prenatal classes or workshops to learn about various aspects of pregnancy and parenthood. Being informed and prepared can help alleviate anxiety and promote a positive pregnancy experience.
Remember, each pregnancy is unique, and your healthcare provider will tailor your prenatal care based on your specific needs. Open communication, adherence to medical advice, and self-care are key elements in maintaining good health during pregnancy.
Fetal Development
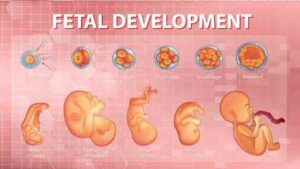
During pregnancy, the fetus undergoes remarkable development and growth. From a tiny cluster of cells to a fully formed baby, this journey is awe-inspiring. Here are the different stages of fetal development:
- Germinal Stage (Weeks 1-2):
- Conception occurs when the sperm fertilizes the egg, forming a zygote.
- The zygote undergoes cell division and travels through the fallopian tube to the uterus.
- Implantation takes place as the zygote attaches to the uterine wall.
- Embryonic Stage (Weeks 3-8):
- The embryo develops three layers: the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.
- Major organs and body systems start to form, including the neural tube, heart, limbs, and facial features.
- By the end of the eighth week, the embryo is about an inch long and resembles a tiny human.
- Fetal Stage (Weeks 9-40):
- During this stage, the developing organism is referred to as a fetus.
- Organs continue to grow and mature, and body systems become more functional.
- The fetus undergoes rapid growth, and external features, such as fingers, toes, and genitals, become distinct.
- By the end of the first trimester, all major organs are present.
- Throughout the second and third trimesters, the fetus continues to grow, and its movements become more pronounced.
- By the end of the pregnancy, the average weight of a full-term baby is around 7 to 8 pounds.
- Milestones in Fetal Development:
- Week 12: The fetus has fully formed genitals, and the external sex organs are distinguishable.
- Week 16: The fetus begins to exhibit reflexes, such as sucking and swallowing.
- Week 20: The fetus is covered in fine hair called lanugo, and vernix, a protective waxy coating, develops on the skin.
- Week 24: The fetus reaches the age of viability, where it has a chance of survival outside the womb with medical intervention.
- Weeks 28-32: The fetus grows rapidly, and its movements become more frequent and vigorous.
- Weeks 36-40: The fetus continues to develop and prepares for birth, assuming the head-down position in the uterus.
Throughout the stages of fetal development, the mother plays a crucial role in providing a nurturing environment. A healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, regular prenatal care, and avoiding harmful substances contribute to the optimal development of the fetus. Each stage of fetal development is vital, and any concerns or abnormalities should be promptly addressed by healthcare professionals.
Understanding the remarkable transformation that occurs during fetal development allows expectant parents to appreciate the journey and bond with their growing baby.
Common Discomforts and Pregnancy Complications
Pregnancy is a beautiful and transformative experience, but it can also come with certain discomforts and complications. Here are some common discomforts and potential complications that pregnant women may encounter:
Common Discomforts
- Morning Sickness: Nausea and vomiting, especially in the first trimester.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and needing more rest than usual.
- Frequent Urination: Increased need to urinate due to hormonal changes and pressure on the bladder.
- Backache: Strain on the back due to the growing belly and shifting posture.
- Heartburn and Indigestion: Increased levels of progesterone can cause digestive issues.
- Swollen Feet and Ankles: Fluid retention leading to swelling in the lower extremities.
- Breast Tenderness: Increased sensitivity and swelling of the breasts.
- Constipation: Slowed digestion and hormonal changes can lead to difficulty passing stools.
- Varicose Veins: Enlarged and twisted veins, often in the legs, due to increased blood volume.
Pregnancy Complications:
Gestational Diabetes: High blood sugar levels during pregnancy, which may require dietary changes and monitoring.
Pre-eclampsia: High blood pressure and organ damage, usually occurring after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Placenta Previa: When the placenta partially or completely covers the cervix, potentially causing bleeding and complications during labor.
Miscarriage: The loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week.
Preterm Labor: Contractions and cervical changes occurring before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Gestational Hypertension: High blood pressure without the presence of protein in the urine, typically occurring after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Preterm Birth: Delivering the baby before 37 weeks of pregnancy, which may result in certain health challenges for the baby.
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: Abnormal growth of cells in the uterus, including conditions like molar pregnancy and choriocarcinoma.
Ectopic Pregnancy: When the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube.
It is essential for pregnant women to communicate with their healthcare provider about any discomforts or concerns they experience during pregnancy. Regular prenatal check-ups and monitoring can help detect and manage potential complications. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, following medical advice, and seeking timely medical attention are key in ensuring a safe and healthy pregnancy.
Pregnancy Safety Guidelines:
During pregnancy, it’s important to prioritize your health and the well-being of your growing baby. Here are some pregnancy safety guidelines to help you have a healthy and successful pregnancy:
Regular Prenatal Care: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider throughout your pregnancy. Prenatal visits allow your healthcare provider to monitor your health, track the development of your baby, and address any concerns or complications that may arise.
Healthy Diet: Eat a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Ensure you’re getting essential nutrients like folic acid, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. Avoid foods that may pose a risk of foodborne illnesses, such as undercooked meats, raw seafood, unpasteurized dairy products, and certain types of fish high in mercury.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay properly hydrated. Adequate hydration is important for the functioning of your body and the development of your baby.
Exercise Regularly: Engage in safe and moderate exercise during pregnancy, with your healthcare provider’s approval. Regular physical activity can help improve circulation, boost mood, manage weight gain, and prepare your body for labor.
Avoid Harmful Substances: Steer clear of alcohol, tobacco, and recreational drugs during pregnancy. These substances can pose serious risks to the health of your baby and increase the chances of complications.
Medication Safety: Consult with your healthcare provider before taking any medications, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements. Some medications may not be safe during pregnancy and could harm your baby.
Manage Stress: Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, meditation, gentle exercise, or seeking support from loved ones. Chronic stress can have an impact on your health and the development of your baby.
Environmental Hazards: Avoid exposure to harmful chemicals, toxins, and radiation. This includes avoiding certain cleaning products, pesticides, lead-based paint, and excessive exposure to sun or heat.
Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently to prevent the spread of germs and reduce the risk of infections. Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing your teeth regularly.
Rest and Sleep: Get enough rest and prioritize sleep to support your overall well-being and allow your body to recover and rejuvenate.
Remember, every pregnancy is unique, and it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance. Following these safety guidelines can help promote a healthy pregnancy and increase the chances of a positive birth experience for you and your baby.
Note: This information is intended for educational purposes only and should not replace medical advice. If you have specific concerns or questions, please consult with a healthcare professional.