Antenatal Care | Overview and guideline
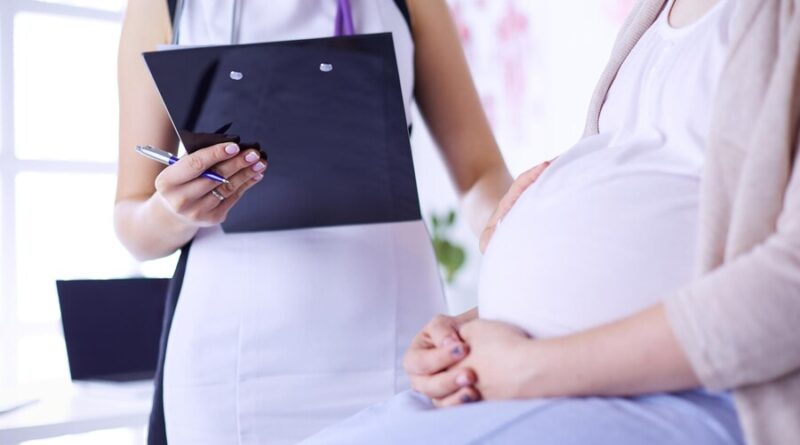
Antenatal care, often referred to as prenatal care, is a vital component of maternal and fetal healthcare. It encompasses a range of medical, educational, and supportive services provided to pregnant individuals to ensure a healthy pregnancy and a positive birth outcome. This comprehensive approach to care involves regular medical check-ups, screenings, education, and guidance to monitor and promote the well-being of both the pregnant person and the developing fetus. In this article, we will delve into the importance of antenatal care, its key components, guidelines, and its role in promoting maternal and child health.
Importance of Antenatal Care

Antenatal care plays a crucial role in identifying and addressing potential risks and complications early in pregnancy. This proactive approach allows healthcare providers to offer timely interventions, reducing the likelihood of complications that could adversely affect the health of the pregnant person and the baby. Regular antenatal visits also provide an opportunity for health professionals to educate pregnant individuals about nutrition, exercise, labor, delivery, and postpartum care. This knowledge equips expectant parents to make informed decisions, leading to healthier pregnancies and safer childbirth experiences.
Key Components of Antenatal Care
- Medical Check-ups and Screenings: Regular medical check-ups are the cornerstone of antenatal care. These appointments involve monitoring the health of the pregnant person and assessing the growth and development of the fetus. Healthcare providers may perform physical examinations, measure blood pressure, monitor weight gain, and conduct various screenings such as blood tests, ultrasounds, and genetic tests to detect any potential complications.
- Nutritional Guidance: Proper nutrition during pregnancy is essential for the health of both the mother and the baby. Antenatal care includes guidance on maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients such as folic acid, iron, calcium, and protein. These nutrients are vital for the development of the baby’s organs and overall growth.
- Education and Counseling: Antenatal care offers educational sessions and counseling on a range of topics, including breastfeeding, childbirth preparation, postpartum depression, and infant care. These sessions empower pregnant individuals with knowledge, helping them navigate pregnancy, childbirth, and parenthood with confidence.
- Emotional and Psychological Support: Pregnancy can be an emotionally charged period, and antenatal care recognizes the importance of emotional well-being. Healthcare providers offer support and guidance to address anxieties, fears, and emotional changes that pregnant individuals may experience.
- Monitoring High-Risk Pregnancies: Some pregnancies are considered high-risk due to pre-existing medical conditions or other factors. Antenatal care closely monitors these pregnancies, implementing specialized interventions as necessary to ensure the safety of both the pregnant person and the baby.
Guidelines for Antenatal Care
- Early Initiation of Care: Antenatal care should ideally commence in the first trimester of pregnancy. Early initiation allows healthcare providers to establish a baseline for health and address any existing medical conditions.
- Regular and Scheduled Visits: Pregnant individuals should attend all recommended antenatal visits as scheduled by their healthcare provider. These visits are spaced to monitor the progression of pregnancy and the health of both mother and baby.
- Personalized Care: Each pregnancy is unique, and antenatal care should be tailored to individual needs. Healthcare providers consider factors such as age, medical history, and any existing conditions to provide personalized care and guidance.
- Health Promotion: Antenatal care promotes a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy. This includes advice on diet, exercise, avoiding harmful substances, and maintaining good hygiene to prevent infections.
- Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness: Pregnant individuals are educated about the signs of labor, what to expect during childbirth, and when to seek medical assistance. This prepares them for a smooth labor and delivery process.
- Postpartum Planning: Antenatal care often includes discussions about postpartum care, including breastfeeding, contraception, and emotional well-being. Planning for the postpartum period ensures a seamless transition into parenthood.
Antenatal care is a fundamental aspect of maternal and fetal healthcare that significantly contributes to positive pregnancy outcomes. Its comprehensive approach, encompassing medical care, education, and support, ensures the well-being of both the pregnant person and the developing baby. By following established guidelines and attending regular visits, expectant parents can take proactive steps towards a healthier pregnancy and a safer childbirth experience. The importance of antenatal care cannot be overstated, as it sets the foundation for a healthy start to the journey of parenthood.