10 principles of Breastfeeding
Principles of Breastfeeding – Breastfeeding is a natural and beautiful way for mothers to provide the best nutrition and care for their infants. It is a remarkable journey that not only nourishes a child’s body but also creates a unique bond between mother and baby. The World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF recommend exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of an infant’s life and continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to two years or beyond.
A non-breastfed child is 14 times more likely to die in the first six months
than an exclusively breastfed child, according to The Lancet.
Breast milk gives a baby everything they need
and costs only what it takes to feed the mother.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the ten fundamental principles of breastfeeding, covering everything from its health benefits to the challenges that may arise, and how to overcome them.
10 Principles of Breastfeeding
10 principles of Breastfeeding are given as follows:
Principle 1: Start Early – The Golden Hour
The journey of breastfeeding begins the moment your baby is born. This is often referred to as “the golden hour.” Skin-to-skin contact during this time is crucial as it helps initiate breastfeeding. Babies are often alert and eager to latch on during the first hour after birth. The colostrum, the first milk, is rich in nutrients and immune-boosting factors that provide your baby with the best start in life.
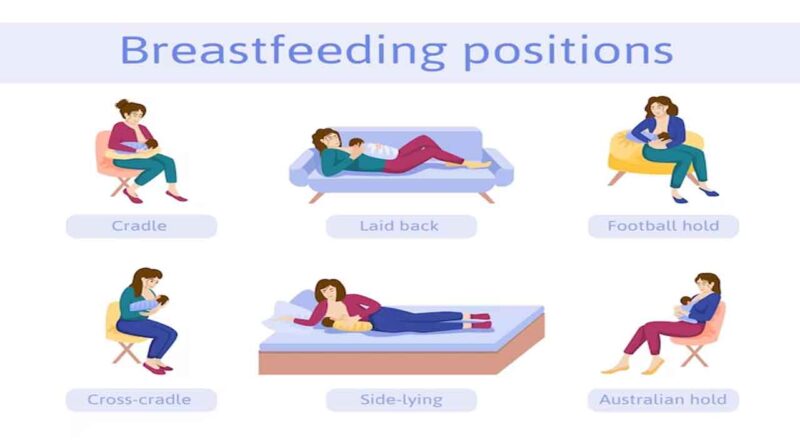
Principle 2: Proper Latch and Positioning
A proper latch is essential for successful breastfeeding. Ensure that your baby has a wide mouth and takes in as much of the areola (the dark area around the nipple) as possible. This not only helps with efficient milk transfer but also prevents nipple soreness. Experiment with various positions, such as the cradle hold, football hold, or side-lying, to find what works best for you and your baby.
Principle 3: Feed on Demand
Breastfeeding is a demand-and-supply system. Feeding your baby on demand, rather than on a strict schedule, ensures your baby gets enough milk. This is especially crucial during the first few weeks when your baby is establishing your milk supply. Signs of hunger include rooting, lip-smacking, and putting their hand to their mouth. Respond to these cues promptly.
Principle 4: Exclusive Breastfeeding for the First Six Months
The WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life. This means that your baby receives only breast milk, with no other food or drink, not even water. Breast milk is perfectly designed to meet all your baby’s nutritional needs during this period.
Principle 5: Understand Your Milk Supply
It’s common for mothers to worry about their milk supply, but understanding how it works can help ease those concerns. The more your baby nurses, the more milk your body produces. Additionally, breast milk production follows a supply and demand cycle. If you’re concerned about low milk supply, it’s important to seek support from a lactation consultant or your healthcare provider.
Principle 6: Breastfeeding Benefits for Mother and Baby
Breastfeeding offers a myriad of benefits for both mother and baby. For infants, it provides essential nutrients and antibodies that protect against infections and allergies. Breastfed babies are less likely to develop respiratory infections, ear infections, and gastrointestinal problems. Mothers who breastfeed experience reduced postpartum bleeding, faster postpartum weight loss, and a decreased risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
Principle 7: Challenges and Solutions
While breastfeeding is a beautiful journey, it can come with challenges. Common issues include sore nipples, engorgement, and difficulties with latching. The good news is that most breastfeeding challenges can be overcome with proper guidance and support. Seek help from a lactation consultant or a support group for breastfeeding mothers to address any issues you may encounter.
Principle 8: Pumping and Storing Breast Milk
Sometimes, mothers need to pump and store breast milk for various reasons, such as returning to work or sharing feeding responsibilities with a partner. Understanding how to pump effectively and store breast milk safely is essential. It’s also important to know that breastfeeding directly from the breast is different from using a breast pump, and you may need to adapt your technique.
Principle 9: Introducing Solid Foods
Around six months of age, you can begin introducing complementary foods while continuing to breastfeed. Start with single-ingredient, iron-rich foods and gradually progress to a variety of textures and flavors. Breast milk should remain an essential part of your baby’s diet, as it continues to provide essential nutrients and immune protection.
Principle 10: Breastfeeding Beyond the First Year
Breastfeeding doesn’t have to end at six months. The WHO recommends continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to two years or beyond. Extended breastfeeding offers numerous benefits, including enhanced immunity, comfort, and bonding between mother and child. It’s essential to respect your child’s needs and your comfort level when deciding how long to breastfeed.
Breastfeeding is a remarkable journey that provides the best start in life for your baby while offering numerous benefits for mothers as well. The ten principles of breastfeeding outlined in this comprehensive guide are crucial to ensuring a successful and fulfilling breastfeeding experience. Remember, breastfeeding is a learned skill, and it’s perfectly normal to seek support and guidance along the way. The journey of nourishing your baby through breastfeeding is not only about providing essential nutrients but also about creating a deep and lasting bond that will benefit both you and your child for a lifetime.